- 59, Parry Compound Road, Katoor, Mettupalayam, Tamil Nadu-641301.
- Mon - Sun : 24 Hours
- 04254-359268
Departments
Cardiology is a medical specialty and a branch of internal medicine concerned
with disorders of the heart.
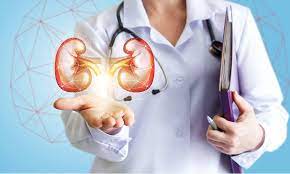
The Department of Nephrology deals
with acute and chronic diseases affecting the kidneys.
SGK Hospital is an exclusive specialty
psychiatry and psychology hospital with admission facility.
Gynaecology focuses on health of female
reproductive system – vagina, uterus, ovaries and breasts.
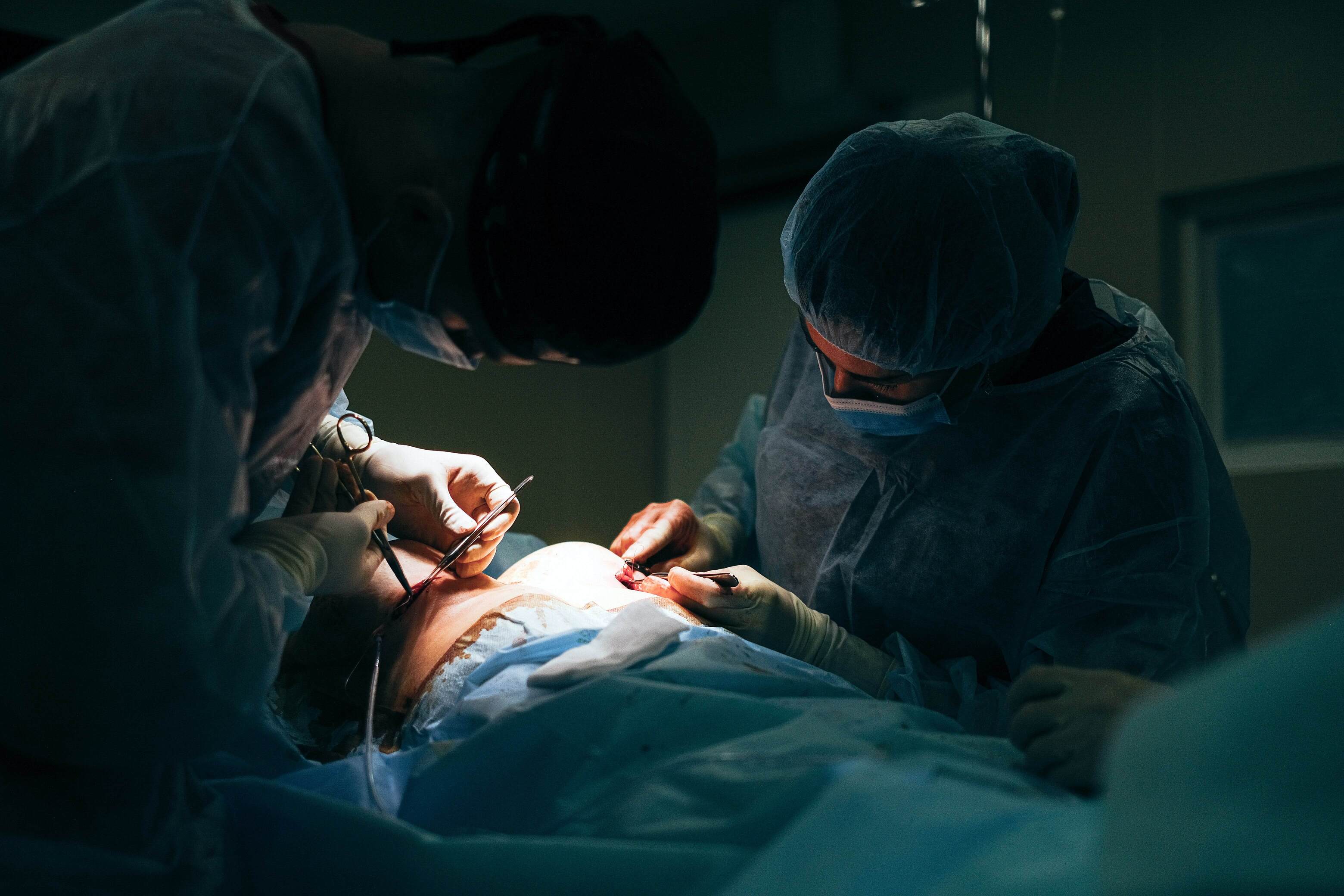
General Surgery focusses on
abdominal procedures which includes esophagus, stomach, small intestine,etc.
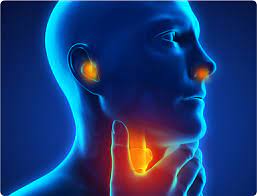
ENT also termed as Otorhinolaryngology,
specializes in management of conditions involving ear,nose and throat.
The Department of Radiology at SGK
Hospital offers a dedicated team of radiologists and healthcare experts .